

| Topic: Scaffolding as Guardrails - Acceptable for Fall Protection | Issued by: Director, Compliance and Regulatory Review |
| Statute: General Regulation 91-191 | Date Issued: May 1, 2016 |
| Section: 49(1), 49(6)(a), 50(2), 97 and 131(1) | Date Revised: July 18, 2024 |
Question:
I am a roofing contractor and I want to use scaffolding with guardrails as my means of fall protection. Is this acceptable?
Answer:
As long as the scaffolding and guardrails meet all the requirements in regulation 91-191, there are several scenarios where properly guarded scaffolding can be a means of fall protection.
They include:
Special Notes: Guardrails are never permitted on surfaces exceeding 6 in 12 pitch. Also, when guarded scaffolding is used as the fall protection method for employees on the roof, employees are not allowed to work from the scaffolding (except for access and egress). In all the scenarios, proper access and egress to the scaffolding and the roof must be provided.
1. Roof pitch less than or equal to 3 in 12
The vertical outside posts, along with the top rail, intermediate rails and toe board provide the foundation of the scaffold system that forms the guardrail. To protect employees that may be working on the roof, the roof projection (which is the floor for the guardrail system for the employees on the roof) is used to determine the railing’s location. The scaffold platform can be up to one metre (1m) below the roof edge. The toe board, intermediate rail and top rail must be installed based on the position of the platform on the scaffold. It is possible that the roof projection intersects with a railing intended to protect the employees on the scaffolding. The platform must be constructed to prevent employees from falling into any openings. The guardrail must provide sufficient strength and rigidity to support an employee who may fall off a roof.
Note: The two options for a roof pitch of up to 6 in 12 can also be used for a pitched roof of less than or equal to 3 in 12 (see below).


Figure #1
2. Roof pitch up to 6 in 12
Option One: In this method, the inside vertical post is extended to the roof’s lower edge and a guardrail is installed. This provides a guarded roof to the employees working on the roof. To provide the required strength and rigidity, a transversal (dogleg) brace should be used. The distance from the roof edge and the guardrails must be as closed as possible to prevent employees falling into the opening. The height of the toe board, intermediate rail and top rail must be determined by projecting the roof line. The projected roof line is considered the floor of the scaffold.

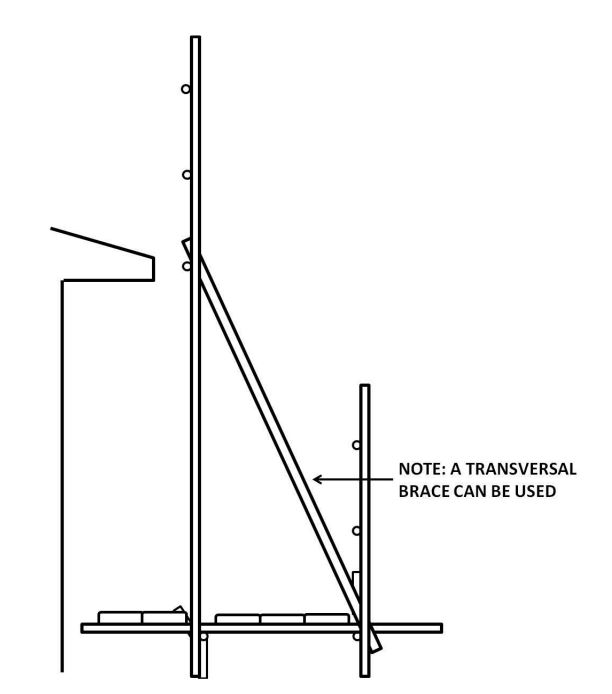
Figure #2 : Option One - Roof pitch up to 6 in 12 using scaffolding for fall protection
Option Two – The inside post of the scaffolding must reach to the lowest edge of the roof and a guardrail is installed above the edge. To ensure the required strength and rigidity, a transversal (dogleg) brace must also be installed. The distance between the roof edge and the guardrail must be as small as possible to prevent employees from falling into the opening. The projected roof line is considered the floor and the height of the toe board, intermediate rail and top rail on the guardrail are determined from that height.
When a roof slope exceeds 3 in 12, the potential for sliding down the roof becomes greater. The horizontal and vertical gaps between the work platform and the roof edge should be as small as possible, and never be large enough for a person to fall through the gap. If employees are working below the scaffolding, the gap must also not allow objects to fall through the gap.

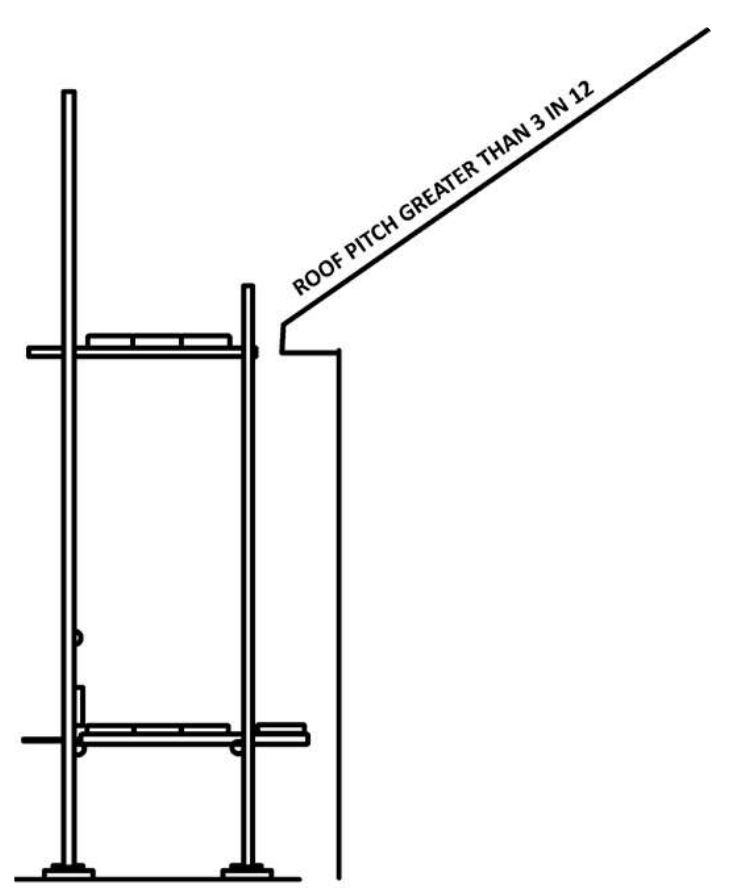
Figure #3 : Option Two - Location of scaffold platform for edge protection (roof pitch greater than 3 in 12)
3. Roof edge protection on gable ends
Edge protection must be provided as close as possible on the gable ends. The top rail should be between 900mm and 1.07m above the line of the gable (slope of the roof). If the work performed on the roof is weatherproofing, a toe board is not required but is recommended. Ensure the scaffold is secured to the building to prevent overturning should someone fall from the roof and strike the guardrails. This can be done by using raking tubes to tie to the building.

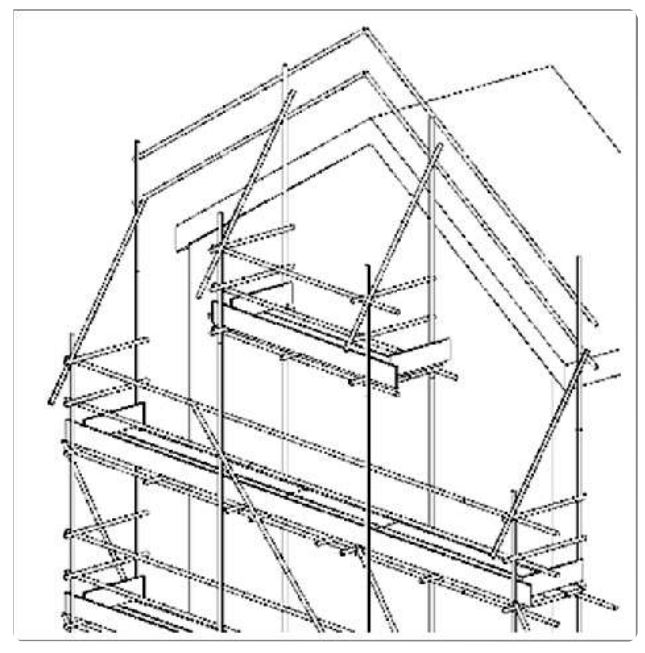
Figure 4: Edge protection at gable ends
Additional things to consider when controlling the hazards of working on a roof:
More information on scaffolding requirements in New Brunswick is included in the OHS Guide to Legislation. http://ohsguide.worksafenb.ca/topic/scaffolding.html
Referenced Legislation
“competent” means
(a) qualified, because of such factors as knowledge, training and experience, to do assigned work in a manner that will ensure the health and safety of persons,
(b) knowledgeable about the provisions of the Act and the regulations that apply to the assigned work, and
(c) knowledgeable about potential or actual danger to health or safety connected with the assigned work;
“weatherproofing” means the application of tar, asphalt, gravel, insulation, shingles or membrane material to a roof but does not include the installation of decking material or the stripping of materials from the roof.
49(1) The employer shall provide and the employee shall continually use a fall-protection system when an employee works from
(a) an unguarded work area that is
(b) a work area that is 3 m or more above a permanent safe level and from which a person may fall if the work area tips or fails, or
(c) a work area where an officer has determined that it is necessary for safety reasons to use a fall-protection system.
49(6) This section does not apply to the following situations:
(a) if the employee will at all times remain further than 3 m from the unguarded edge of a surface with a slope of 3 in 12 or less;
50(2) Despite subsection (1), the use of a guardrail is not permitted on a surface that has a slope exceeding 6 in 12.
97(1) A guardrail shall
(a) be made of one of the following materials:
(A) the top rail, vertical supporting posts and intermediate rail shall be constructed of at least 50 mm × 100 mm No. 2 grade or better SPF, these measures being nominal, and
(B) shall not be painted other than by a transparent protective coating,
(A) the top rail and vertical supporting posts shall be at least 40 mm in diameter, and
(B) the intermediate rail shall be at least 25 mm diameter,
(A) the top rail and vertical supporting posts shall be at least 40 mm × 40 mm by 5 mm, and
(B) the intermediate rail shall be at least 32 mm × 32 mm × 3 mm, or
(A) the vertical supporting posts shall be made of steel of at least 40 mm in diameter or of a material of equivalent strength, and
(B) the top rail and intermediate rail shall be at least 10 mm in diameter, be attached to a welded fastening on the vertical supporting posts with metal clips to prevent unnecessary sagging and be easily distinguishable from the background; or
(b) be pre-engineered.
97(2) A guardrail shall
(a) have a height of not less than 900 mm or more than 1.07 m from the floor level,
(b) have a toeboard which
(i) is at least 127 mm high,
(ii) is fastened to the inside of the vertical supporting posts, and
(iii) has a space of not more than 6 mm between the bottom of the toeboard and the floor,
(c) have vertical supporting posts not more than 2.4 m apart along its entire length unless otherwise specified in manufacturer’s specifications, and
(d) have vertical supporting posts not more than 3 m apart along its entire length if the guardrail is used on scaffolding.
97(3) The vertical supporting posts referred to in paragraphs 2(c) and (d) shall be adequately fastened to the structure to support the loads imposed upon it.
97(4) Unless the guardrail is a pre-engineered guardrail, the top rail shall be fastened to the top or inside of the vertical supporting posts and the intermediate rail shall be fastened to the inside of the vertical supporting posts midway between the top rail and the floor level.
97(5) A guardrail shall be made of materials with sufficient strength and rigidity to support loads with the following minimums:
| (a) | 675 N in any direction, at any point along the top rail; | ||
| (b) | 450 N in any direction, at any point along the intermediate rail; and | ||
| (c) | 900 N in any direction, at any point along the top rail, intermediate rail and toeboard if the guardrail is used on a surface that is sloped more than 3 in 12 and less than 6 in 12. |
127 Measurements of lumber in sections 131 to 142, other than measurements for sawn lumber planks, are nominal.
131(1) An employer and a contractor shall each ensure that a scaffold
| (a) | is capable of sustaining a minimum uniformly distributed load of 1.4 kPa, | ||
| (b) | is at no time subjected to a load that exceeds the equivalent of one-quarter of the load for which it is designed, | ||
| (c) | is designed and constructed to support at least four times the load that may be imposed on it, | ||
| (d) | if 3 m or more in height, has a guardrail that meets the requirements of section 97, | ||
| (e) | is erected plumb and level, | ||
| (f) | has vertical supports resting upon a firm foundation or sills, | ||
| (g) | is adequately secured at vertical intervals not exceeding three times the least lateral dimension of the scaffold, measured at the base, to prevent lateral movement, | ||
| (h) | if sawn lumber planks are used as a platform, has a platform that is at least 500 mm wide, and | ||
| (i) | if using manufactured scaffold planks, has a platform that is at least 450 mm wide. |
Content based on information from WorkSafe New Zealand.